lshw (list hardware) command is a small tool that generates detailed reports about various hardware components, including CPU version, memory configuration, cache information, bus speed, etc. on the system.
- lshw command is able to do so because it reads various files located in the /proc directory.
- To display complete information you must be root user or super user. Else it will print partial information.
Syntax of lshw Command
lshw [format] [options]
Format:
- -html: Output hardware tree as HTML
- -xml: Output hardware tree as XML
- -json: Output hardware tree as a JSON object
- -short: Output hardware paths
- -businfo: Output bus information
Options:
- class: Only show a certain class of hardware
- enable: Enable a test (like pci, isapnp, cpuid, etc. )
- disable: Disable a test (like pci, isapnp, cpuid, etc. )
- quiet: Don’t display status
- sanitize: Sanitize output (remove sensitive information like serial numbers, etc.)
- numeric: Output numeric IDs (for PCI, USB, etc.)
- notime: Exclude volatile attributes (timestamps) from output
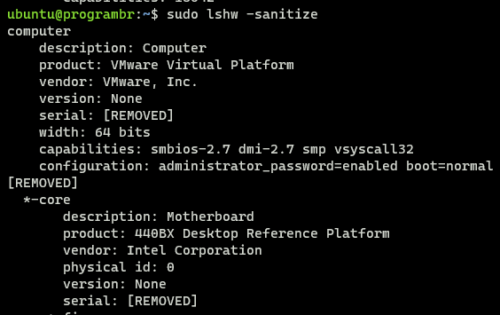
Display full hardware information
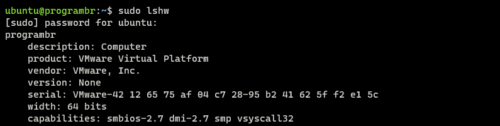
To display complete hardware information use lshw command without any options and format.
sudo lshw
lshw help
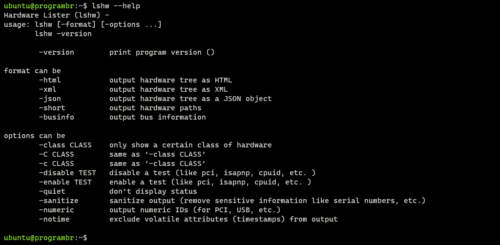
To get help related to “lshw” command, use the command “lshw –help”. It will help you find the format and options available with “lshw” command.
lshw --help
lshw format
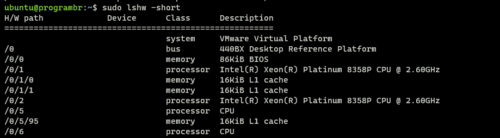
Display hardware path
Use “lshw” command followed by “-short” to display hardware path in a compact format.
sudo lshw -short
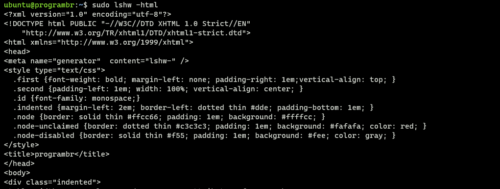
Display information in HTML
Use “lshw” command followed by “-html” to display hardware information in HTML format.
sudo lshw -html
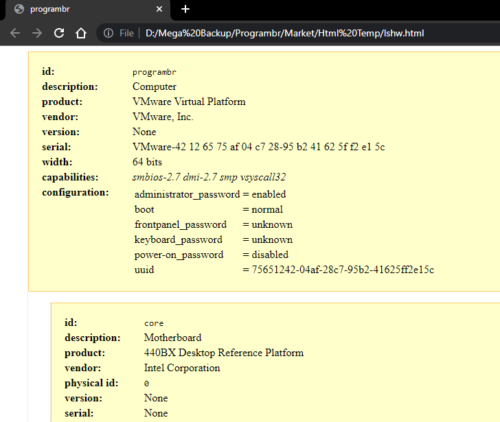
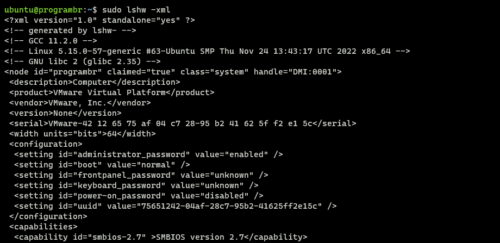
Display information in XML format
Use “lshw” command followed by “-xml” to display hardware information in XML format.
sudo lshw -xml
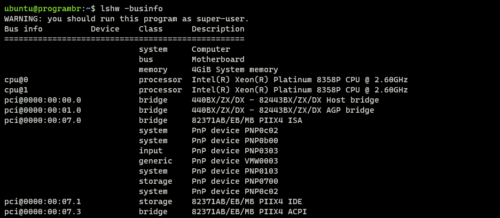
Display bus information
Use “lshw” command followed by “-businfo” to display the bus information. It provides more information about the SCSI, USB, IDE, PCI etc.
lshw -businfo
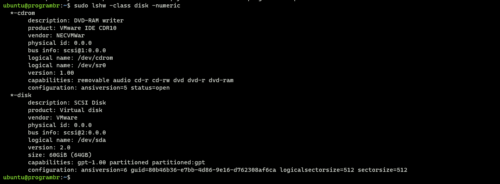
lshw options
sudo lshw -class disk -numeric
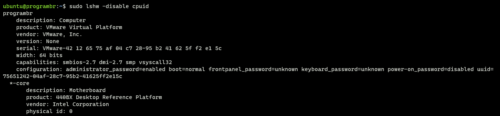
lshw command with -disable option allow us to disable various parameter’s functionality .
Here I am disabling cpuid.
sudo lshw -disable cpuid
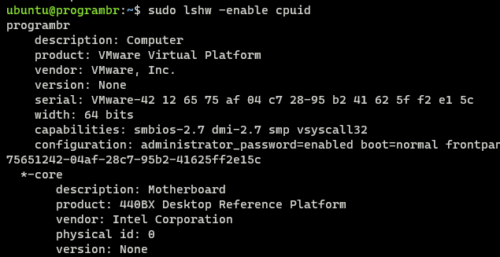
lshw command with -enable option allow us to enable various parameter’s functionality.
Here I am enabling cpuid.
sudo lshw -enable cpuid
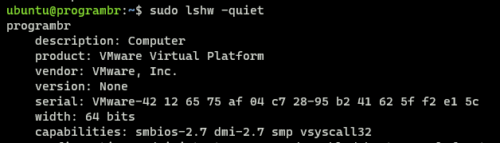
sudo lshw -quiet
sanitize is used, When users don’t wish to display sensitive information. Use the lshw command with -sanitize option to hide sensitive information like serial numbers, IP addresses etc.
sudo lshw -sanitize
A |
| adduser | addgroup | alias | anacron | apt | aptitude | arp | at | atq | atrm | awk |
B |
| basename | banner | batch | bc | bg | bzip |
C |
| cat | cal | cd | chgrp | chown | cksum | chmod | clear | cmp | comm | cp |
D |
| date | dd | df | diff | dir | dmidecode | du |
E |
| echo | eject | env | exit | expr |
F |
| factor | find | free |
G |
| grep | groups | gunzip | gzip |
H |
| head | history | hostname | hostnamectl | htop | hwclock | hwinfo |
I |
| id | ifconfig | ionice | iostat | ip | iptables | iw | iwlist |
J |
K |
| kill | kmod |
L |
| last | less | ln | locate | login | lp | ls | lshw | lscpu | lsof | lsusb |
M |
| man | mdsum | mkdir | more| mv |
N |
| nano | nc | neofetch | netcat | netstat | nice | nmap | nproc |
O |
| openssl |
P |
| passwd | pidof | ping | pr | ps | pwd | pstree |
Q |
R |
| rdiff-backup | reboot | rename | rm | rmdir | rnmod |
S |
| scp | shred | shutdown | sleep | sort | split | ssh | stat | su | sudo | sum |
T |
| tac | tail | talk | tar | tee | time | tree | top | touch | tr |
U |
| unalias | uname | uniq | unzip | uptime | users |
V |
| vim | vi |
W |
| w | wall | watch | wc | wget | whatis | whereis | which | who | whoami |
X |
| xargs |
Y |
| yes | youtube-dl |
Z |
| zcmp | zdiff | zip | zz |