wall command is used to broadcast the messages or the contents of a file to all the currently logged-in users on the terminals in the Linux system. The message can be typed on the terminal or the contents of a file. When superuser or root user broadcast the messages, all users receive the messages. In this tutorial, you are going to learn about wall command in Linux / Ubuntu.
** If no message or file is specified, wall command broadcast the message from the stdin (standard input).
** The broadcasted messages are shown to all logged-in users on terminal. Users using a graphical desktop environment with no terminal open will not see the messages.
wall command in Linux with examples
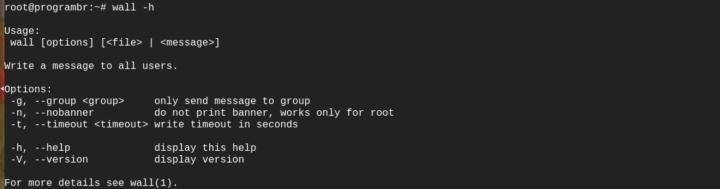
- wall -h: This will display help message.
wall -h
2. wall -v: This will display wall version information.
wall -V
Broadcasting Message Using wall command
Wall Command Syntax
The syntax for using wall command in terminal is written below.
wall [OPTIONS] [<FILE>|<MESSAGE>]wall : This will broadcast text you type or text from the file.
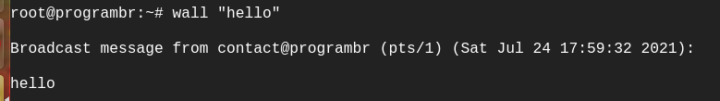
wall "hello"
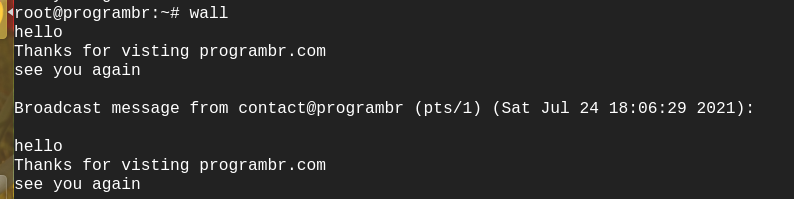
** If you want to broadcast multi-line messages, just write wall command in terminal and hit Enter. After that type the text, that you want to broadcast in the terminal and press CTRL+D.
wall hello Thanks for visting programbr.com see you again
Output:
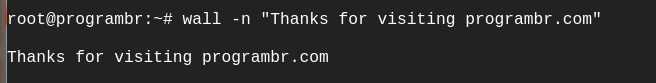
wall -n : This will suppress the banner and show only the text you type or text from the file.
wall -n "Thanks for visiting programbr.com"
Output:
wall [-n] [-t timeout] [message | file]
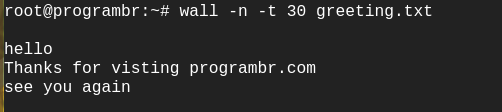
wall -n -t 30 greeting.txt
Output:
Broadcast the contents of a file using wall command
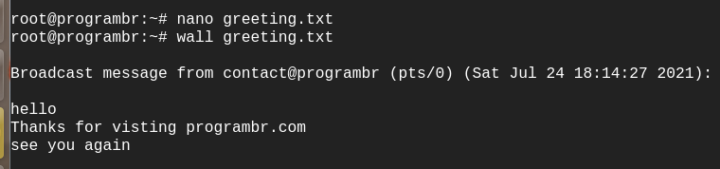
To broadcast the contents of a file use wall filename command in terminal.
wall greeting.txt
Conclusion
I hope that You have learned how to use wall command in Linux. wall command is used to broadcast the messages or the contents of a file to all the currently logged-in users on the terminals in the Linux system.